SJI Grantee Spotlights

New Mexico Supreme Court Assessment of Bar Licensure and Rural Access
The Supreme Court of New Mexico, with generous assistance from SJI, has convened a committee dedicated to the development of an alternative, supervised-practice means of licensure that focuses on a skills-based assessment of a bar applicant’s legal abilities. The National Center for State Courts, as contractor on the project, assisted the committee by gathering information about similar models in other states and surveying local interested persons so that the qualifications and requirements of the program fit the needs of New Mexico. The committee expects to provide a final report to the New Mexico Supreme Court this spring.
While a two-day written examination has been used for decades, new reports questioning its efficacy in assessing a bar applicant’s readiness to practice law prompted the New Mexico Supreme Court to explore additional means of admitting attorneys to the practice.
Under the program, candidates must graduate from an accredited law school and will receive a conditional license to practice law upon acceptance. Candidates then work with a supervisor to submit regular work product for review by the Board of Bar Examiners to determine the candidate’s competence to practice. A candidate proves their practice readiness with actual legal work product and may begin working and earning a paycheck much sooner. For supervisors, this program will provide a pool of candidates who are able to practice upon graduation while also giving rural practitioners a new recruitment tool to encourage attorneys to practice in different parts of the state.

National Judicial Task Force to Examine State Courts’ Response to Mental Illness
January 1, 2023
On March 30, 2020, the Boards of Directors of the Conference of Chief Justices and Conference of State Court Administrators took action to establish National Judicial Task Force to Examine State Courts Response to Mental Illness to assist state courts in their efforts to more effectively respond to the needs of court-involved individuals with serious mental illness. …
Puerto Rico Judicial Branch Electronic Court
December 1, 2022
During the pandemic, the Puerto Rico Office of Courts Administration (OCA) created an email account through which self-represented litigants (SRLs) seeking an emergency restraining order, a temporary detention or an involuntary admission order related to the Mental Health Code could file their petition to the Municipal Court. SRLs could download, complete, and submit the applicable …

Convening County, Court & Justice Leaders: A Framework for Cross-System Collaboration Initiative
November 1, 2022
In January 2022, the National Association of Counties, Rulo Strategies, and Praxis Consulting launched a new initiative to support justice-oriented strategic planning co-led by judges and elected county leaders. This timely project leveraged the renewed interest many courts have, coming out of the pandemic, in partnering with local stakeholders to expand the resources available to …

Kentucky’s Responsive Education to Support Treatment in Opioid Recovery Efforts (RESTORE)
October 1, 2022
In 2020, the Kentucky Administrative Office of the Courts (AOC) received a SJI grant to assess the court’s access to and use of mental health and substance use recovery services within the community. Funding allowed the Crime and Justice Institute (CJI) to conduct an assessment of strengths, opportunities and challenges that judges, court personnel and …
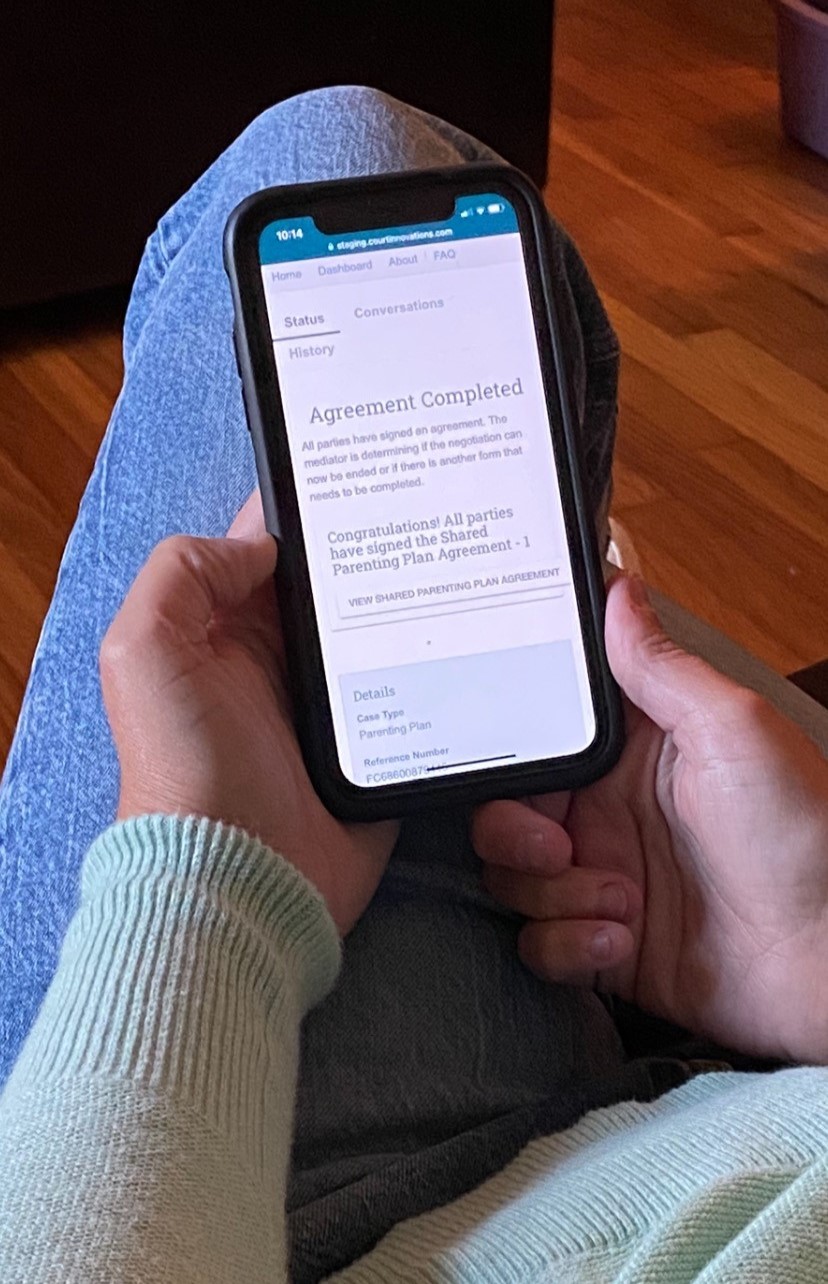
The Supreme Court of Ohio – Ohio ODR Pilot Program
September 1, 2022
The emergence of COVID-19 has had widespread effects throughout the court system and quarantine orders slowed operations. The Supreme Court of Ohio anticipated an influx of evictions and foreclosure filings in Ohio’s trial courts, as well as a backlog of civil cases. Chief Justice Maureen O’Connor directed the Office of Court Services to convene stakeholders …

King County Superior Court, Washington – The Response of the King County Superior Court to the COVID-19 Pandemic: Lessons Learned and Recommendations
August 1, 2022
King County, Washington, was ground zero for the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. The Washington State Supreme Court suspended most court operations in all courts on March 18, 2020. Acknowledging access to justice is of critical importance, King County Superior Court (KCSC) leadership vowed to continue to hold matters on all …

